The Challenge
Recently, at a client, I was challenged to create a stored procedure that would process a tabular model. This stored procedure would then be executed from a web application. The process behind it being: a user enters data into a web application, which gets written to a database. That data then needs to be immediately surfaced up into reports, with additional calculations and measures along the way. Therefore the tabular model, which does all the additional calculation and measures, needs to be processed by a user from the web application.
That’s the challenge – process a tabular model quickly, but should be processed by users on-demand.
The Solution
Part one: Method of process
There’s quite a few methods to process a tabular model: use an SSIS package, PowerShell, SQL Agent Job and others. I opted for SQL Agent Job because it was the most simple method of execution without having to reconfigure the server or introduce technologies and languages that weren’t already in use.
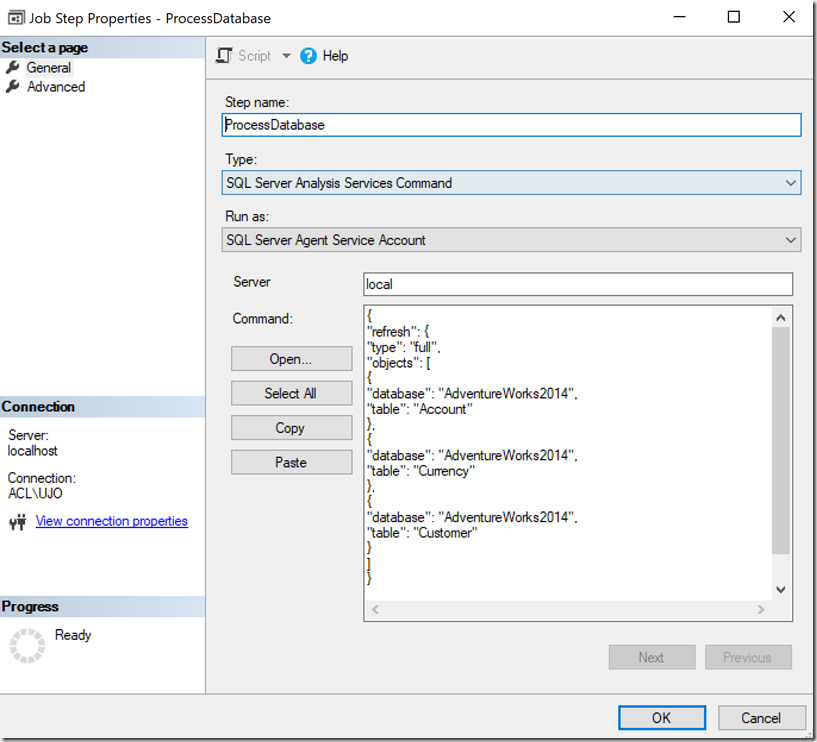
First things first, create a SQL Agent Job, I called mine ProcessTabular. Then create a Step. The Type should be SQL Server Analysis Services Command, input the server address and input the refresh script. I’m using SQL Server 2016, so using Tabular Model Scripting Language (TMSL) for my command. XMLA commands also work for older versions. A full list of commands for processing a tabular database can be found here.
Part two: Start the Agent Job
Now that we have a SQL Agent job, we’ll need to start that job using SQL. Luckily, there’s a system stored procedure that can start agent jobs: msdb.dbo.sp_start_job
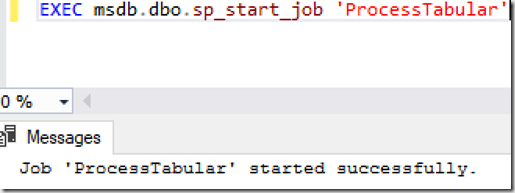
Method for calling it is
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_start_job 'ProcessTabular'
producing the following successful message
Part three: The Stored Procedure
sp_start_job works, but it doesn’t accommodate for providing a completion message, or informing a user that a process is in progress.
Introducing the code for the stored procedure:
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[ProcessTabularDatabase]
AS
DECLARE @JobName nvarchar(50) = 'ProcessTabular',
@ResultCheck INT
IF NOT EXISTS(
SELECT 1
FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobs_view job
JOIN msdb.dbo.sysjobactivity activity ON job.job_id = activity.job_id
WHERE
activity.run_Requested_date IS NOT NULL
AND activity.stop_execution_date IS NULL
AND job.name = @JobName
)
BEGIN
PRINT 'Starting job ''' + @JobName + '''';
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_start_job @JobName;
WHILE (1 = 1)
BEGIN
SELECT @ResultCheck = IIF(stop_execution_date IS NULL,1,0)
FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobactivity AS sja
JOIN msdb.dbo.sysjobs AS sj ON sja.job_id = sj.job_id
WHERE sj.name = @JobName
IF @ResultCheck = 0 BREAK;
END
PRINT 'Successfully Processed Tabular Database'
END
ELSE
BEGIN
PRINT 'Job ''' + @JobName + ''' is already started ';
END
Conclusion
This stored procedure can be executed by the web application, enabling users to process a tabular database on-demand and get feedback as to the success of the task.

Introduction to Data Wrangler in Microsoft Fabric
What is Data Wrangler? A key selling point of Microsoft Fabric is the Data Science
Jul
Autogen Power BI Model in Tabular Editor
In the realm of business intelligence, Power BI has emerged as a powerful tool for
Jul
Microsoft Healthcare Accelerator for Fabric
Microsoft released the Healthcare Data Solutions in Microsoft Fabric in Q1 2024. It was introduced
Jul
Unlock the Power of Colour: Make Your Power BI Reports Pop
Colour is a powerful visual tool that can enhance the appeal and readability of your
Jul
Python vs. PySpark: Navigating Data Analytics in Databricks – Part 2
Part 2: Exploring Advanced Functionalities in Databricks Welcome back to our Databricks journey! In this
May
GPT-4 with Vision vs Custom Vision in Anomaly Detection
Businesses today are generating data at an unprecedented rate. Automated processing of data is essential
May
Exploring DALL·E Capabilities
What is DALL·E? DALL·E is text-to-image generation system developed by OpenAI using deep learning methodologies.
May
Using Copilot Studio to Develop a HR Policy Bot
The next addition to Microsoft’s generative AI and large language model tools is Microsoft Copilot
Apr